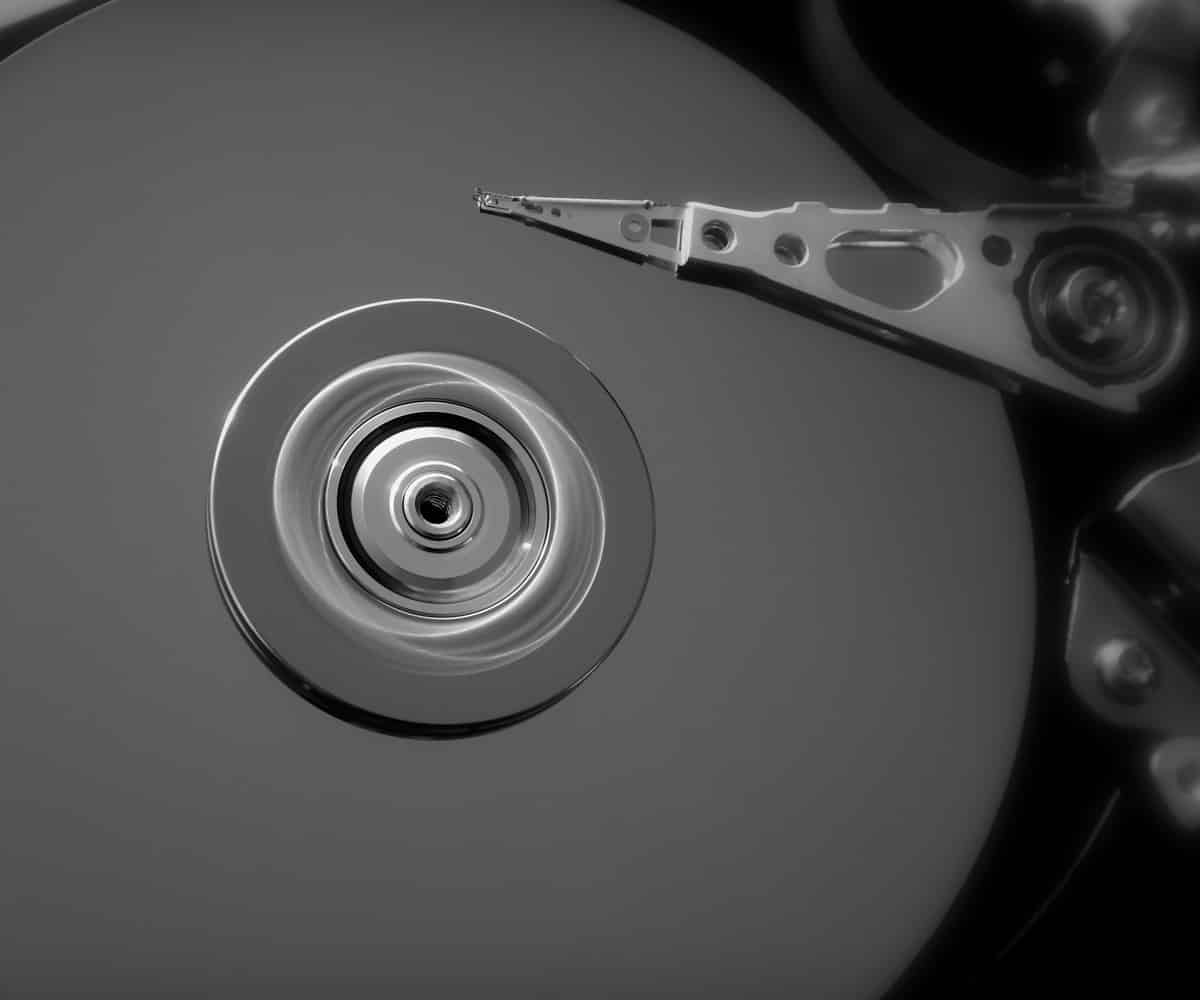
Hard drive failure can be a frustrating and potentially devastating experience for both individuals and businesses alike. Symptoms of hard drive failure can range from minor issues to complete data loss, making it important to be aware of the warning signs.
One common symptom of hard drive failure is slow performance. If a computer or device is taking longer than usual to boot up or load programs, it could be a sign that the hard drive is failing. Additionally, frequent crashes or freezes can also indicate a problem with the hard drive.
Another symptom of hard drive failure is strange or unusual noises coming from the device. Clicking, grinding, or whirring sounds can be a sign of physical damage to the hard drive, which can result in data loss if not addressed promptly. It is important to back up important data regularly to avoid losing it in the event of a hard drive failure.
Recognizing Hard Drive Failure
Hard drive failure can be a frustrating and expensive issue to deal with. It can lead to data loss and system crashes, making it essential to know the warning signs of a failing hard drive. Here are some of the most common symptoms to look out for:
Warning Signs
One of the most obvious signs of hard drive failure is when your computer displays error messages, freezes, crashes, or shows a blue screen of death. These warning signs may not always be caused by a failing hard drive, but they are usually an indication that something is wrong.
Strange Noises
Another sign of hard drive failure is strange noises coming from your computer. If you hear clicking or grinding sounds, it could be a sign that the hard drive is failing. These noises are usually caused by the read/write head repeatedly trying to access data on a damaged or failing disk.
Physical Damage Signs
Physical damage to the hard drive can also lead to failure. Signs of physical damage include dents, cracks, or other visible damage to the hard drive. If you notice any physical damage, it’s important to address the issue immediately to prevent further damage.
Performance Issues
A failing hard drive can also cause performance issues. If your computer is running slower than usual, taking longer to boot up, or experiencing frequent freezes or crashes, it could be a sign of hard drive failure. Overheating can also cause performance issues and can be a sign of a failing hard drive.
In conclusion, recognizing the warning signs of hard drive failure is essential to prevent data loss and system crashes. If you notice any of the symptoms mentioned above, it’s important to address the issue immediately to avoid further damage.
Understanding Hard Drive Failures
When a hard drive fails, it can be a frustrating and stressful experience. Understanding the different types of hard drive failures can help you identify the issue and determine the best course of action.
Mechanical Failures
Mechanical failures occur when there is physical damage to the hard drive. This can happen when the hard drive is dropped or bumped, or when there is a motor failure. Mechanical hard drives have moving parts, so any damage to these parts can cause the hard drive to fail.
Symptoms of mechanical failure include clicking or grinding noises coming from the hard drive, as well as the computer freezing or crashing. If you suspect a mechanical failure, it is important to stop using the hard drive immediately to prevent further damage.
Electrical Surges
Electrical surges can also cause hard drive failure. This can happen when there is a power outage or when the computer is not properly grounded. Solid-state drives (SSDs) are particularly susceptible to electrical surges.
Symptoms of electrical surges include the computer not turning on or the hard drive not being recognized by the computer. To prevent electrical surges, it is important to use a surge protector and ensure that your computer is properly grounded.
Logical Failures
Logical failures occur when there is a software issue with the hard drive. This can happen when there is a virus or malware on the computer, or when there are file system errors. Logical failures can affect both mechanical and solid-state hard drives.
Symptoms of logical failures include slow computer performance, error messages when accessing files, and the computer freezing or crashing. To prevent logical failures, it is important to regularly backup your files and run antivirus software.
In conclusion, understanding the different types of hard drive failures can help you identify the issue and determine the best course of action. Whether it is a mechanical failure, electrical surge, or logical failure, it is important to take immediate action to prevent further damage to your hard drive and data.
Diagnostic Tools and S.M.A.R.T.

When it comes to detecting hard drive failure, diagnostic tools and S.M.A.R.T. (Self-Monitoring, Analysis, and Reporting Technology) are essential. Here are some of the diagnostic tools that can help:
S.M.A.R.T. Status
S.M.A.R.T. is a monitoring system built into most modern hard drives. It can detect and report various indicators of drive health, such as temperature, read/write errors, and bad sectors. Checking the S.M.A.R.T. status of a drive can give an early warning of potential failure.
To check the S.M.A.R.T. status of a drive, users can use software such as CrystalDiskInfo or Hard Disk Sentinel. These tools provide a detailed report of the drive’s health status, including any errors or warnings.
Using Chkdsk
Chkdsk (short for “check disk”) is a built-in Windows tool that can scan and repair file system errors on a hard drive. It can also detect and mark bad sectors, which can help prevent further damage to the drive.
To use Chkdsk, users can open a command prompt and type “chkdsk /f” followed by the drive letter. This will initiate a scan and repair process on the selected drive.
Other Diagnostic Software
In addition to S.M.A.R.T. monitoring and Chkdsk, there are many other diagnostic tools available for hard drives. Some of these tools include DiskCheckup, which can detect and report S.M.A.R.T. errors and provide a health status report, and HD Tune, which can perform a variety of tests on a hard drive, including a surface scan and benchmarking.
Overall, using diagnostic tools and monitoring the S.M.A.R.T. status of a hard drive can help detect and prevent potential failure. It is important to regularly check and maintain the health of hard drives to ensure data integrity and prevent data loss.
Data Protection Strategies

When it comes to protecting your data, prevention is always better than cure. In this section, we will discuss some effective data protection strategies that can help you avoid data loss due to hard drive failure.
Regular Backups
One of the most effective ways to protect your data is to create regular backups. By backing up your data, you can ensure that you always have a copy of your important files in case your hard drive fails. You can create backups manually or use backup software to automate the process. It is recommended to create backups on a regular basis, such as daily, weekly, or monthly, depending on your needs.
Using Cloud Storage
Cloud storage is another effective data protection strategy that can help you avoid data loss due to hard drive failure. By storing your data in the cloud, you can ensure that it is always accessible from anywhere and on any device. Most cloud storage services offer automatic backups and versioning, which can help you recover your data in case of a hard drive failure.
Professional Recovery Services
If you are unable to recover your data using backup or data recovery software, you may need to seek professional help. Professional data recovery services can help you recover your data from a failed hard drive. These services have specialized equipment and expertise to recover data from damaged or corrupted hard drives. However, professional data recovery services can be expensive, so it is important to weigh the cost against the value of your data.
In conclusion, by following these data protection strategies, you can ensure that your data is safe and secure. Whether you choose to create regular backups, use cloud storage, or seek professional help, it is important to take proactive measures to protect your data from hard drive failure.
Preventive Measures and Maintenance

Operating Environment
The operating environment plays a significant role in the lifespan of a hard drive. High temperatures can cause the hard drive to overheat, leading to damage and failure. It is crucial to ensure that the computer and hard drive are kept in a cool and well-ventilated area. Avoid placing the computer in direct sunlight or near a heat source.
Handling and Storage
Proper handling and storage of the hard drive can prevent damage and extend its lifespan. Always handle the hard drive with care and avoid dropping it. When storing the hard drive, keep it in a safe and dry place, away from any moisture or dust.
Regular Cleaning and Updates
Regular cleaning of the computer and hard drive can prevent dust buildup, which can cause overheating and damage to the hard drive. Use a soft, dry cloth to clean the hard drive and computer, and avoid using any harsh chemicals or abrasive materials.
Updating the computer’s software and operating system can also prevent hard drive failure. Regular updates can fix any bugs or issues that may cause the hard drive to malfunction.
In addition, using a surge protector can protect the hard drive from power surges and spikes, which can cause damage and failure. It is recommended to use a surge protector to prevent any damage to the hard drive during power outages or lightning strikes.
By following these preventive measures and maintenance tips, users can extend the lifespan of their hard drive and prevent hard drive failure.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
When it comes to hard drive failure, there are a few common issues that users may encounter. Here are some troubleshooting tips for addressing bad sectors, resolving system crashes, and correcting data corruption.
Addressing Bad Sectors
Bad sectors can occur when a portion of the hard drive becomes damaged or unreadable. This can result in data loss or system crashes. To address bad sectors, users can run a disk check utility such as chkdsk. This utility will scan the hard drive for errors and attempt to repair any bad sectors.
Resolving System Crashes
System crashes can occur when the operating system encounters an error or when a hardware component fails. If the hard drive is the culprit, users may experience freezes or crashes. To resolve system crashes, users can try reinstalling the operating system or resetting the computer to its factory settings. If the issue persists, it may be necessary to replace the hard drive.
Correcting Data Corruption
Data corruption can occur when files become damaged or unreadable. This can result in lost or corrupted data. To correct data corruption, users can try running a disk check utility such as chkdsk. This utility will scan the hard drive for errors and attempt to repair any corrupted files. If the issue persists, users may need to reinstall the affected software or restore their data from a backup.
Overall, it is important to regularly back up important data and monitor the health of the hard drive to prevent and address any potential issues.
When to Replace the Drive
There are several reasons why a hard drive may need to be replaced. In this section, we will discuss the most common scenarios that may require replacing the drive.
End of Lifespan
Like any other hardware, hard drives have a limited lifespan. Over time, the wear and tear of constant use can cause the drive to fail. As a general rule of thumb, hard drives should be replaced every 3 to 5 years. If the drive is older than this, it may be time to consider replacing it.
After Recurring Failures
If a hard drive has experienced recurring failures, it may be time to replace it. Mechanical failures, such as a damaged read/write head or spindle motor, can cause the drive to fail repeatedly. In some cases, it may be possible to recover data from a failing drive, but it is always best to replace the drive as soon as possible to avoid further data loss.
Upgrade Considerations
If you are upgrading your computer, it may be necessary to replace the hard drive. For example, if you are upgrading from a traditional hard drive to a solid-state drive, you will need to replace the existing drive. Similarly, if you are upgrading to a larger capacity drive, you will need to replace the existing drive.
In conclusion, there are several scenarios where it may be necessary to replace a hard drive. Whether due to wear and tear, aging, mechanical failures, or an upgrade, replacing the drive can help ensure the longevity and reliability of your computer system.
External Factors and Hard Drive Failure
When it comes to hard drive failure, there are several external factors that can contribute to it. In this section, we will discuss some of the most common external factors that can lead to hard drive failure.
Environmental Impacts
One of the most common external factors that can cause hard drive failure is environmental impact. This can include exposure to extreme temperatures, humidity, or even dust. When a hard drive is exposed to extreme temperatures or humidity, it can cause the components to expand or contract, leading to physical damage. Dust can also accumulate on the hard drive’s internal components, causing overheating and eventually leading to failure.
Power Issues
Power issues can also contribute to hard drive failure. Power surges, for example, can cause the hard drive’s electrical components to fail, leading to data loss or corruption. Similarly, sudden power outages can cause the hard drive to shut down abruptly, potentially leading to damage to the drive’s components.
Human Errors and Viruses
Human errors and viruses can also cause hard drive failure. Accidentally deleting important files or formatting the wrong drive can lead to data loss. Viruses and malware can also infect the hard drive, causing data corruption or even physical damage to the drive’s components.
Overall, it is important to take precautions to protect your hard drive from external factors that can lead to failure. This can include using surge protectors, keeping your computer in a clean and dust-free environment, and regularly backing up important data. By taking these steps, you can help ensure the longevity and reliability of your hard drive.